
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen, China
2 Shanghai Jiao Tong University, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai, China
3 University of L’Aquila, Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, L’Aquila, Italy
We propose a joint look-up-table (LUT)-based nonlinear predistortion and digital resolution enhancement scheme to achieve high-speed and low-cost optical interconnects using low-resolution digital-to-analog converters (DACs). The LUT-based predistortion is employed to mitigate the pattern-dependent effect (PDE) of a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA), while the digital resolution enhancer (DRE) is utilized to shape the quantization noise, lowering the requirement for the resolution of DAC. We experimentally demonstrate O-band intensity modulation and direct detection (IM/DD) transmission of 124-GBd 4 / 6-level pulse-amplitude modulation ( PAM ) -4 / 6 and 112-GBd PAM-8 signals over a 2-km standard single-mode fiber (SSMF) with 3 / 3.5 / 4-bit DACs. In the case of 40-km SSMF transmission with an SOA-based preamplifier, 124-GBd on-off-keying (OOK)/PAM-3/PAM-4 signals are successfully transmitted with 1.5 / 2 / 3-bit DACs. To the best of our knowledge, we have achieved the highest net data rates of 235.3-Gb / s PAM-4, 289.7-Gb / s PAM-6, and 294.7 Gb / s PAM-8 signals over 2-km SSMF, as well as 117.6-Gb / s OOK, 173.8-Gb / s PAM-3, and -231.8 Gb / s PAM-4 signals over 40-km SSMF, employing low-resolution DACs. The experimental results reveal that the joint LUT-based predistortion and DRE effectively mitigate the PDE and improve the signal-to-quantization noise ratio by shaping the noise. The proposed scheme can provide a powerful solution for low-cost IM/DD optical interconnects beyond 200 Gb / s.
look-up-table digital resolution enhancer quantization noise semiconductor optical amplifier pattern-dependent effect pulse-amplitude modulation Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(3): 036007
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai, China
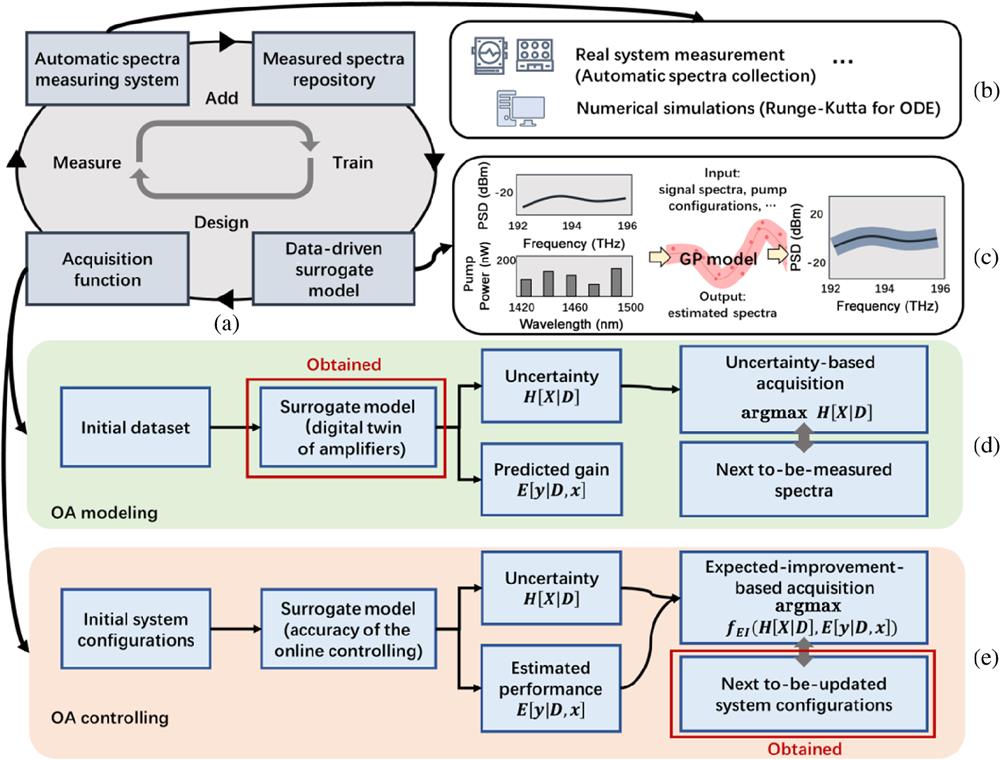
Optical networks are evolving toward ultrawide bandwidth and autonomous operation. In this scenario, it is crucial to accurately model and control optical power evolutions (OPEs) through optical amplifiers (OAs), as they directly affect the signal-to-noise ratio and fiber nonlinearities. However, a fundamental contradiction arises between the complex physical phenomena in optical transmission and the required precision in network control. Traditional theoretical methods underperform due to ideal assumptions, while data-driven approaches entail exorbitant costs associated with acquiring massive amounts of data to achieve the desired level of accuracy. In this work, we propose a Bayesian inference framework (BIF) to construct the digital twin of OAs and control OPE in a data-efficient manner. Only the informative data are collected to balance the exploration and exploitation of the data space, thus enabling efficient autonomous-driving optical networks (ADONs). Simulations and experiments demonstrate that the BIF can reduce the data size for modeling erbium-doped fiber amplifiers by 80% and Raman amplifiers by 60%. Within 30 iterations, the optimal controlling performance can be achieved to realize target signal/gain profiles in links with different types of OAs. The results show that the BIF paves the way to accurately model and control OPE for future ADONs.
optical fiber communications digital twin Bayesian inference optical amplifiers autonomous-driving optical networks Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(2): 026006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518055, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 School of Electronics and Information Technology and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Processing Chips and Systems, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China
4 e-mail: yixiaozhu@sjtu.edu.cn
5 e-mail: xueyang.li@pcl.ac.cn
Data centers, the engines of the global Internet, rely on powerful high-speed optical interconnects. In optical fiber communication, classic direct detection captures only the intensity of the optical field, while the coherent detection counterpart utilizes both phase and polarization diversities at the expense of requiring a narrow-linewidth and high-stability local oscillator (LO). Herein, we propose and demonstrate a four-dimensional Jones-space optical field recovery (4-D JSFR) scheme without an LO. The polarization-diverse full-field receiver structure captures information encoded in the intensity and phase of both polarizations, which can be subsequently extracted digitally. To our knowledge, our proposed receiver achieves the highest electrical spectral efficiency among existing direct detection systems and potentially provides similar electrical spectral efficiency as standard intradyne coherent detection systems. The fully recovered optical field extends the transmission distance beyond the limitations imposed by fiber chromatic dispersion. Moreover, the LO-free advantage makes 4-D JSFR suitable for photonic integration, offering a spectrally efficient and cost-effective solution for massively parallel data center interconnects. Our results may contribute to the ongoing developments in the theory of optical field recovery and the potential design considerations for future high-speed optical transceivers.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(3): 399

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai, China
Chaotic optical communication has shown large potential as a hardware encryption method in the physical layer. As an important figure of merit, the bit rate–distance product of chaotic optical communication has been continually improved to 30 Gb/s × 340 km, but it is still far from the requirement for a deployed optical fiber communication system, which is beyond 100 Gb/s × 1000 km. A chaotic carrier can be considered as an analog signal and suffers from fiber channel impairments, limiting the transmission distance of high-speed chaotic optical communications. To break the limit, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a pilot-based digital signal processing scheme for coherent chaotic optical communication combined with deep-learning-based chaotic synchronization. Both transmission impairment recovery and chaotic synchronization are realized in the digital domain. The frequency offset of the lasers is accurately estimated and compensated by determining the location of the pilot tone in the frequency domain, and the equalization and phase noise compensation are jointly performed by the least mean square algorithm through the time domain pilot symbols. Using the proposed method, 100 Gb / s chaotically encrypted quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) signal over 800 km single-mode fiber (SMF) transmission is experimentally demonstrated. In order to enhance security, 40 Gb / s real-time chaotically encrypted QPSK signal over 800 km SMF transmission is realized by inserting pilot symbols and tone in a field-programmable gate array. This method provides a feasible approach to promote the practical application of chaotic optical communications and guarantees the high security of chaotic encryption.
chaotic optical communication physical layer security deep learning digital signal processing Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(1): 016003
1 浙江大学现代光学仪器国家重点实验室光及电磁波研究中心, 浙江 杭州 310027
2 Department of Physics, Mcgil University, Canada
设计并制作了一种基于激光直写工艺的多模高聚物1×8光功率分配器。该器件采用了独特的次级非对称结构实现了光功率在各个输出端口的均匀分配。借助紫外激光直写的方式, 配合高精度平移台实现了器件的加工, 并将整个分配器的制作过程控制在5 min以内, 从而在加工周期上颇具优势。对所得的分配器进行了性能测试, 实验结果表明, 端口输出光功率最大均匀度差异小于4%, 证明了器件具有较为理想的分光性能。提出的激光直写法结构加工无需掩模或离子蚀刻等复杂加工手段, 有助于大幅度提高制造效率并能够有效地控制器件性能。
激光直写 非对称 高聚物 功率分配器





